Organs of the immune system
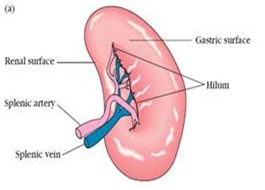
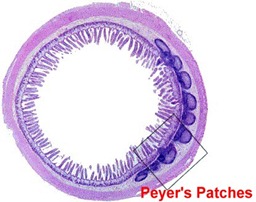
The immune system can be distinguished by function as the: Primary Lymphoid organs --> Thymus & Bone marrow Secondary lymphoid organs –> Lymph nodes , Spleen & Various Mucosal Lymphoid Tissues (MALT ), such as Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT ). Tertiary lymphoid organs –> Cutaneous-associated lymphoid tissues Primary Lymphoid organs: Only after a lymphocyte has matured a primary lymphoid organ is the cell immune competent. In mammals, T-cells mature in the " Thymus " and B-cells mature in the " Bone marrow ” (in Bursa of Fabricus in birds). There are TWO cells in the Primary Lymphoid Organs – Thymus and Bone Marrow . Secondary lymphoid organs Lymph nodes and the spleen are the most highly organized of the secondary lymphoid organs. Less-organized lymphoid tissue, collectively called " Mucosal-Associated lymphoid Tissue"(MALT) , is found in various body sites. MALT includes -...